It is recently reported that several employees of LG Energy Solution (Nanjing) Co., Ltd. (LGES) have posted on social platforms about significant layoffs in November. The termination documents released by these employees show that they signed agreements with LGES in early November, stipulating that their labor relations would officially end on November 20th, with the company providing a one-time financial compensation. According to information provided by multiple employees, the compensation standard is N+3, where N represents the number of years the employee has worked at the company.
In response, on November 13th, LGES stated that the recent online circulation of information regarding personnel changes within the company is part of normal employee adjustments under normal business operations, not the mass layoffs as rumored. LGES explained that the purpose of this adjustment is to optimize production line arrangements to enhance core competitiveness in response to changes in the market environment. However, LGES did not disclose the specific scale of the labor adjustment at the Nanjing production base.
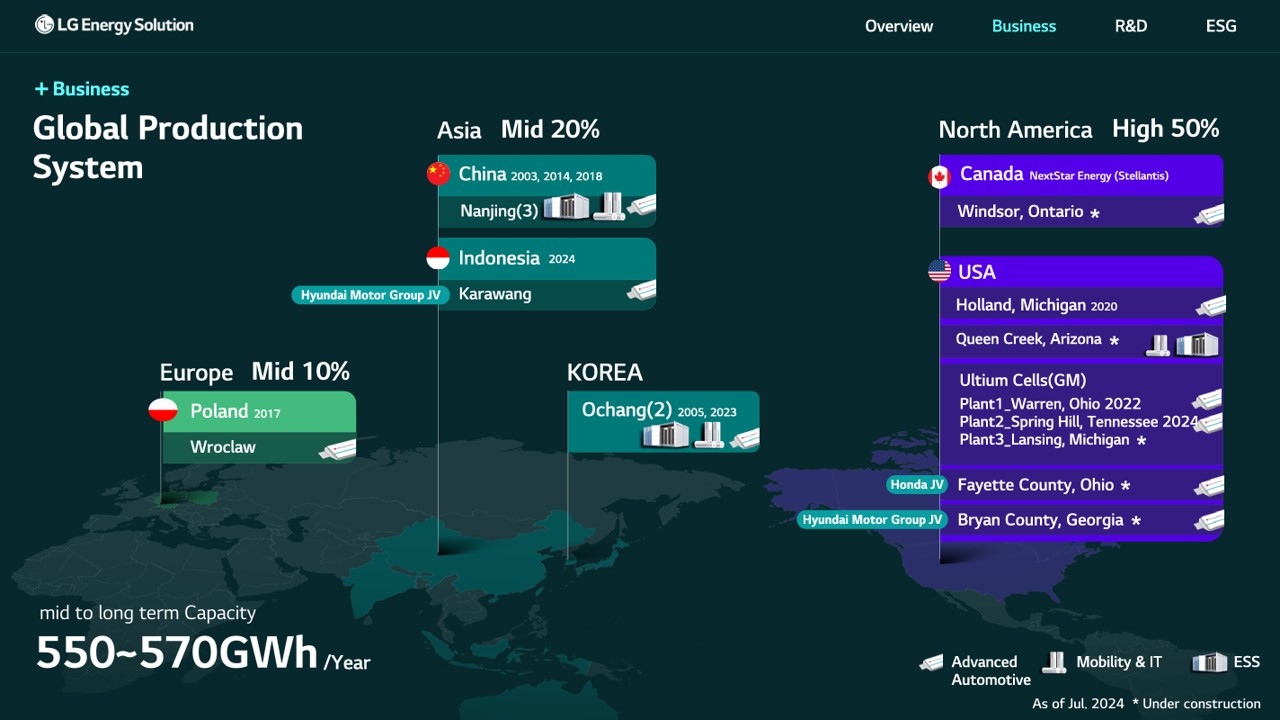
Records show that LG Energy Solution (Nanjing), established in 2003, is a wholly-owned subsidiary of LG New Energy and is the largest battery manufacturing base of LG New Energy in China. It mainly engages in the production, manufacturing, and sales of electric vehicle (EV) batteries and energy storage (ESS) batteries. Currently, LG Energy Solution (Nanjing) has three battery factories in the XinGang Development Zone of Qixia District, Nanjing, and the Jiangning Binjiang Development Zone, namely LG Energy Solution (Nanjing) Co., Ltd., LG Energy Solution Battery (Nanjing) Co., Ltd., and LG Energy Solution Technology (Nanjing) Co., Ltd., with a total capacity of 62GWh and a workforce of 10,000 employees.

In 2023, LGES's factory in Jiangning Binjiang Development Zone signed a contract to produce exclusive EV batteries for General Motors. Previously, LGES stated plans to expand the production capacity of the Nanjing factory from 62GWh to 145GWh by 2025. In March of this year, LGES also signed a contract with the Jiangning Binjiang Development Zone for the production of power and energy storage batteries, with a total investment of about $800 million (approximately 5.77 billion RMB). On October 18th, the new production line project of LG Energy Solution, along with other major projects, collectively started construction in the Binjiang Development Zone.
However, affected by the slowdown in global electric vehicle sales, LGES is also under tremendous performance pressure. At the end of July this year, LGES's second-quarter financial report showed that the overall revenue for the second quarter was 61.619 trillion won (approximately 34.231 billion RMB), a 0.5% increase quarter-on-quarter and a 29.8% decrease year-on-year; the operating profit was 19.53 billion won (approximately 1.077 billion RMB), a 24.2% increase quarter-on-quarter and a 57.6% decrease year-on-year, with an operating profit margin of 3.2%. The company expects its business income for 2024 to decrease by more than 20% compared to 2023.
The third-quarter performance announced in October showed a slight improvement, but there was still a significant year-on-year decline: the overall revenue for the third quarter was 68.778 trillion won (approximately 35.35 billion RMB), a 11.6% increase quarter-on-quarter and a 16.4% decrease year-on-year. The operating profit was 44.83 billion won (approximately 2.31 billion RMB), a 129.5% increase quarter-on-quarter and a 38.7% decrease year-on-year.
It is worth mentioning that without considering the U.S. IRA tax credit amount, the company's operating profit for both quarters would be in deficit.
To achieve business growth, in October of this year, LGES made medium- and long-term strategic adjustments: actively expanding from the electric vehicle field to energy storage systems (ESS), urban air mobility (UAM), electric vessels, and robots, and other new businesses with high growth potential, achieving diversification of battery chemistry and customers, expanding software and service businesses to increase revenue sources, and striving to develop solid-state batteries, lithium-sulfur batteries, lithium-metal batteries, and other next-generation battery technologies to ensure leadership in the battery field. LGES plans to better cope with market fluctuations through these measures and achieve the goal of doubling business income by 2028.
Since the second half of this year, LGES has made significant gains in battery customer orders and has signed long-term supply agreements with many well-known car companies in Europe and America.
Just yesterday (November 18th), LGES announced that it had signed a cylindrical battery supply agreement with the U.S. service robot company Bear Robotics.
On November 8th, LGES announced that it had signed a five-year supply agreement with the U.S. electric vehicle startup Rivian for 4695 large cylindrical batteries, supplying a total of 67 GWh of batteries from LGES's battery factory in Arizona, equipped with the R2 model to be launched in 2026.
On October 15th, LGES announced that it had signed two battery supply contracts with Ford Motor Company, supplying a total of 109 GWh of batteries for Ford's electric commercial vans produced in the UK and EU countries from its battery factory in Poland starting in 2026, with a contract term of 4 to 6 years.
On October 8th, LGES signed a ten-year long-term procurement agreement with Mercedes-Benz, from 2028 to 2038, LGES will supply 50.5 GWh of large cylindrical batteries to Mercedes-Benz in North America and other markets.
On July 1st, Ampere, the power battery business department of Renault Group, announced that it would cooperate with LGES and CATL to establish a lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery supply chain in Europe. Among them, LGES will supply 39 GWh of LFP batteries to Ampere from the end of 2025 to 2030, equipped with 590,000 electric vehicles.
Additionally, LGES is also reported to plan to complete a pilot line for dry battery electrode production and begin mass production of 4680 large cylindrical batteries to supply Tesla by the end of this year. In October 2023, LGES announced its intention to increase the cylindrical battery production capacity at its Arizona facility from 27GWh to 36GWh annually. It is anticipated that once fully operational in 2026, the battery production base, including lithium iron phosphate (LFP) energy storage batteries and large cylindrical batteries, will achieve a combined annual capacity of 53GWh.
These substantial order volumes, concentrated in Europe and North America—strategic focal regions for LGES—will significantly aid LGES in achieving its goal of doubling its revenue by 2028. This aligns with LGES's medium- to long-term battery production capacity plans: the company's planned 550 to 570 GWh of battery production capacity will have 50% focused on the North American region.
However, LGES's market share is being eroded. According to statistics from SNE, from January to September this year, the global electric vehicle battery installation reached 599 GWh, a year-on-year increase of 23.4%. Among them, LGES's EV batteries installed volume for the first three quarters of this year was 72.4 GWh, ranking third globally, with a year-on-year increase of 4.3%, and a market share of 12.1%, which is a decline of 2.2 percentage points from 14.3% in the same period last year. In contrast, the top two, CATL (300750.SZ) and BYD (002594.SZ), achieved EV battery installations of 219.6 GWh and 98.5 GWh respectively during the same period, with market shares increasing by 0.9% and 0.5% separately.
In the Chinese market, LGES's market share is also declining. From January to October 2024, LGES's EV battery installation volume in China was 5.82 GWh, ranking 10th, with a market share of 1.62%, a year-on-year decrease of 0.42 percentage points. In comparison, the top two, CATL and BYD, achieved installation volumes of 154.55 GWh and 97.78 GWh respectively, with market shares of 43.01% and 27.21% respectively. CALB, Gotion, SVOLT, Sunwoda, EVE Energy, ZEnergy, and REPT Battero all have higher EV battery installation volumes in China than LGES.
This year, several battery companies have laid off employees, including SK On, SVOLT Energy, and Northvolt, among other domestic and international lithium battery companies that have been reported to have layoffs. Additionally, CATL and CALB are also optimizing their personnel. This reflects the increasing intense competition in the battery industry.
According to media reports, Ouyang Ming, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, predicted that by 2025, the domestic battery production capacity could reach an astonishing 3000 GWh in China, while the shipment volume is expected to be only 1200 GWh, resulting in an industry capacity vacancy rate as high as 60%. According to the latest data from the China Automobile Battery Innovation Alliance, from January to October this year, the cumulative output of EV and other batteries in China was 847.5 GWh, while the cumulative installation volume of EV batteries from January to October was only 405.8 GW, which means that nearly half of the batteries will be stored as inventory. Faced with overcapacity and price wars, the EV battery industry in 2024 faces even more intense competition, and layoffs or personnel reductions have become routine measures for companies to reduce costs and increase efficiency.








